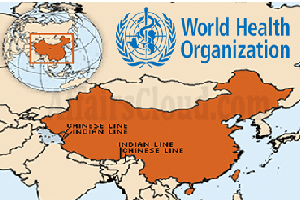
The World Health Organisation map shows the Aksai Chin region as a part of China with a dotted line and colour code. Also marks Pakistan-occupied Kashmir(PoK) with dotted lines, suggesting it as a disputed territory. Jammu and Kashmir(J&K) and the rest of India are marked in different colour codes. Many United Nations (UN) maps have shown parts of Kashmir as ‘disputed’ territory in the past, but this is the 1st time that Ladakh and J&K are shown in different colour codes than the rest of India. The map of China is based on the 1989 edition of the Sky Map of its national borders, though Beijing has resolved its border issues with Russia and Central Asian countries. About WHO: Headquarters– Geneva, Switzerland. Director General (DG)–TedrosAdhanomGhebreyesus.